The Oracle LENGTH() function returns the number of characters of a specified string. It measures the length of the string in characters as defined by the input character set.
Syntax #
The following illustrates the syntax of the Oracle LENGTH() function:
LENGTH(string_expression);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Arguments #
The Oracle LENGTH() function accepts one argument:
string_expression
is the string or an expression that returns a string to be evaluated. The string_expression can be a constant, a variable, or a column of a table.
The data type of string_expression argument can be any of the following data types CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, CLOB, or NCLOB.
Return value #
The LENGTH() function returns a positive integer that represents the number of characters in the string_expression.
If the string_expression is NULL, the LENGTH() function returns NULL.
If the string_expression is CHAR data type, its length will include all leading and trailing blanks.
Examples #
The following statement uses the LENGTH() function to calculate the number of characters of the string 'Oracle LENGTH' using a single-byte database character set:
SELECT
'Oracle LENGTH' string,
LENGTH('Oracle LENGTH') Len
FROM
dual;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)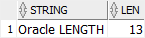
See the following employees table in the sample database:

The following statement sorts the employees by the lengths of their first names. It uses the LENGTH() function in the ORDER BY clause:
SELECT
first_name,
LENGTH(first_name)
FROM
employees
ORDER BY
LENGTH(first_name) DESC;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)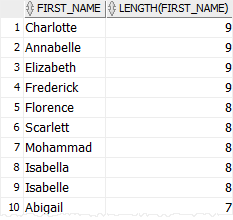
The following statement groups employees by the lengths of their first names. It uses the LENGTH() function in the GROUP BY clause:
SELECT
LENGTH( first_name ) len,
COUNT( * )
FROM
employees
GROUP BY
LENGTH( first_name )
ORDER BY len;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)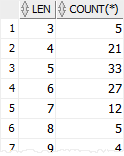
See the following products table:

Suppose, you have to display a list of products with their excerpts on the company’s website.
The following statement uses the LENGTH() function with CONCAT() and SUBSTR() functions to return the excerpts for products.
SELECT
product_name,
CASE
WHEN LENGTH( description ) > 50 THEN CONCAT( SUBSTR( description,
1, 50 ), '...' )
ELSE description
END product_excerpt
FROM
products
ORDER BY
product_name;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If the product description has a length of less than 50, it will be used as the excerpt. Otherwise, the first 50 characters of the description will be used.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Oracle LENGTH() function to get the number of characters of a string.