The Oracle CONCAT() function concatenates two strings and returns the combined string.
Syntax #
The following illustrates the syntax of the CONCAT() function:
CONCAT(string1,string2)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Noted that the Oracle CONCAT() function concatenates two strings only. If you want to concatenate more than two strings, you need to apply the CONCAT() function multiple times or use the concatenation operator (||).
Arguments #
The CONCAT() function accepts two arguments whose data types can by any of the data types CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, CLOB, or NCLOB.
string1
is the first string value to concatenate with the second string value.
string2
is the second string value to be concatenated.
Return Value #
The CONCAT() function returns a string whose character set depends on the character set of the first string argument.
The data type of the result string depends on the data types of the two arguments. Oracle will try to convert the result string in a loss-less manner.
For example, if you concatenate a CLOB value with an NCLOB value, the data type of the returned string will be NCLOB.
Examples #
The following statement concatenates two strings 'Happy' and ' coding':
SELECT
CONCAT('Happy',' coding')
FROM
dual;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)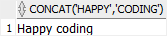
If you want to concatenate more than two strings, you need to apply the CONCAT() function multiple times as shown in the following example:
SELECT
CONCAT( CONCAT( 'Happy', ' coding' ), ' together' )
FROM
dual;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)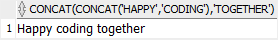
In this example:
- The first
CONCAT()function concatenates two strings:'Happy'and' coding', and returns a result string. - The second
CONCAT()function concatenates the result string of the firstCONCAT()function, which is'Happy coding', with the string' together'that results in'Happy coding together'.
Concatenation operator || #
In addition to the CONCAT() function, Oracle also provides you with the concatenation operator (||) that allows you to concatenate two or more strings in a more readable fashion:
string1 || string2 || string3 || ...
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For example, to concatenate three strings: 'Happy', ' coding', and ' together', you use the concatenation operator (||) as follows:
SELECT
'Happy' || ' coding' || ' together'
FROM
dual;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
See the following employeestable in the sample database:

The following statement uses the concatenation operator to construct the full name of employees from the first name, space, and the last name:
SELECT
first_name || ' ' || last_name
FROM
employees;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)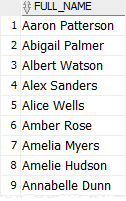
Remarks #
To concatenate strings that contain a single quote (‘), you must escape the single quote by doubling it as shown in the following example:
SELECT
CONCAT('let''s',' try this')
FROM
dual;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this example, the string let's contains a single quote (‘) and we escaped the single quote by doubling it (”).
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the Oracle CONCAT() function to concatenate two strings. You also learned how to use the concatenation operator (||) that concatenates three or more strings.