Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Oracle IN operator to determine whether a value matches any value in a list or a subquery.
Introduction to Oracle IN operator #
The Oracle IN operator determines whether a value matches any values in a list or a subquery.
A subquery is a query nested within another query, you will learn about the subquery in the subquery tutorial.
The syntax of the Oracle IN operator that determines whether an expression matches a list of values is as follows:
expression IN (v1,v2,v3,...)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax:
- The
expressionis any valid expression, which can be a column of a table that you want to match. -
v1, v2, v3..is a list of comma-separated values to test for a match. All the values must have the same data type asexpression.
The IN operator returns TRUE if the value of the expression equals any value in the list. Otherwise, it returns FALSE.
To negate the result of the IN operator, you use the NOT operator:
expression NOT IN (v1,v2,...)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The NOT IN operator returns TRUE if the result of the expression is not IN the list of values (v1, v2, …) and FALSE otherwise.
Typically, you use the IN operator in a WHERE clause for filtering data in a column with a list of values.
Oracle IN operator examples #
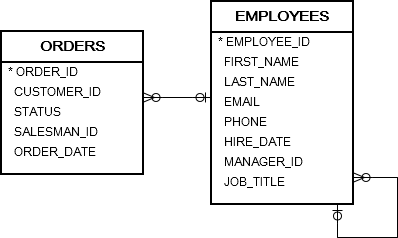
We’ll use the orders and employees tables in the sample database for the demonstration:
Basic Oracle IN operator examples #
The following statement uses the IN operator to find orders which are in charge of the salesman id 54, 55, and 56:
SELECT
order_id,
customer_id,
status,
salesman_id
FROM
orders
WHERE
salesman_id IN (54, 55, 56)
ORDER BY
order_id;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
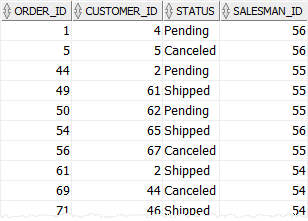
The query returned all orders whose values in the salesman_id column is 54, 55or 56:
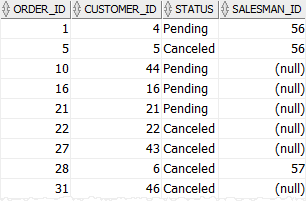
Similarly, the following example uses the IN operator to retrieve the sales orders with the status isPending or Canceled:
SELECT
order_id,
customer_id,
status,
salesman_id
FROM
orders
WHERE
status IN ('Pending', 'Canceled')
ORDER BY
order_id;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
Oracle NOT IN operator example #
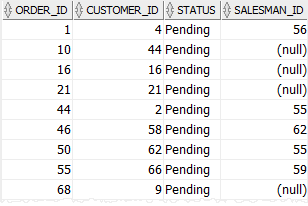
The following statement uses the NOT IN operator to find orders whose statuses are not Shipped and Canceled:
SELECT
order_id,
customer_id,
status,
salesman_id
FROM
orders
WHERE
status NOT IN ('Shipped', 'Canceled')
ORDER BY
order_id;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The result is:
Oracle IN vs. OR #
The following statement uses the IN operator to retrieve the sales orders with the salesman id is 60, 61, or 62:
SELECT
customer_id,
status,
salesman_id
FROM
orders
WHERE
salesman_id IN (60, 61, 62)
ORDER BY
customer_id;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)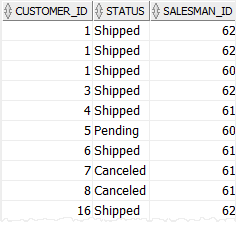
It is equivalent to the following query but uses the OR operator:
SELECT
customer_id,
status,
salesman_id
FROM
orders
WHERE
salesman_id = 60
OR salesman_id = 61
OR salesman_id = 62
ORDER BY
customer_id;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Note that the expression:
salesman_id NOT IN (60,61,62);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)has the same effect as:
salesman_id != 60
AND salesman_id != 61
AND salesman_id != 62;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Summary #
- Use the Oracle
INoperator to query data that matches a list of values - Use the
NOToperator to negate theINoperator.