Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Oracle BETWEEN operator to select rows whose values are in a range of values.
Introduction to Oracle BETWEEN operator #
The BETWEEN operator allows you to specify a range to test. Here’s the syntax of the BETWEEN operator:
expression BETWEEN low AND highCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax:
- The
expressionis a value or column to test if it is in a range of values. To compare, the data types ofexpression,low, andhighmust be comparable. - The
lowandhighspecify the lower and upper values of the range to test. Thelowandhighvalues can be literals or expressions. - The
ANDoperator acts as a placeholder to separate betweenlowandhigh.
The BETWEEN operator returns TRUE if the value of expression is greater than or equal (>=) to low and less than or equal (<=) to high.
value >= low AND value <= highCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To negate the BETWEEN operator, you use the NOT operator. The NOT BETWEEN operator returns TRUE if the value is not in the range of values or FALSE otherwise:
expression NOT BETWEEN low AND highCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In other words, the NOT BETWEEN operator returns TRUE only if the expression less than the low value or greater than the high value:
expression < low OR expression > highCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In practice, you often use BETWEEN operator in the WHERE clause of the SELECT, DELETE, and UPDATE statement.
Oracle BETWEEN operator examples #
Let’s look at some examples of using the Oracle BETWEEN operator.
Oracle BETWEEN numeric values example #
We’ll use the following products table in the sample database:

The following statement uses the BETWEEN operator to return products with standard costs between 504.14 and 538.55:
SELECT
product_name,
standard_cost
FROM
products
WHERE
standard_cost BETWEEN 504.14 AND 538.55
ORDER BY
standard_cost;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
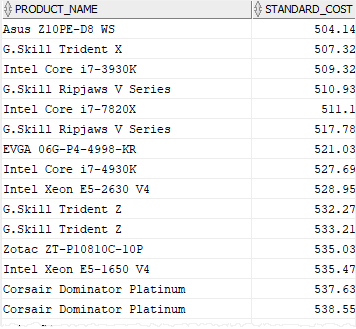
In this example, we compare the values in the standard_cost column with a range from 504.14 to 538.55.
The query returns products whose standard costs are between that range. Notice that the it includes rows with the standard cost are 504.14 and 538.55
To retrieve products whose standard costs are not between 504.14 and 538.55, you use the NOT BETWEEN operator as follows:
SELECT
product_name,
standard_cost
FROM
products
WHERE
standard_cost NOT BETWEEN 504.14 AND 538.55
ORDER BY
product_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
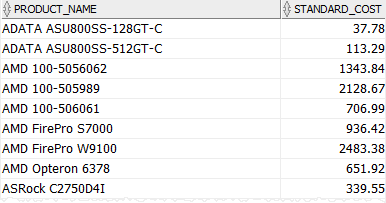
BETWEEN dates problem and solution #
Let’s use the orders table in the sample database for the demonstration:

The following statement returns the orders placed by customers between December 1, 2016, and December 31, 2016:
SELECT
order_id,
customer_id,
status,
order_date
FROM
orders
WHERE
order_date BETWEEN DATE '2016-12-01' AND DATE '2016-12-31'
ORDER BY
order_date;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
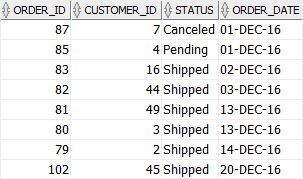
The BETWEEN operator works properly because the order_date column has no time component.
In this example:
DATE '2016-12-01'means2016-12-01 00:00:00.DATE '2016-12-31'means2016-12-31 00:00:00(midnight at the very start ofDecember 31).
The BETWEEN operator is inclusive of both low and high values.
But because the high value is 2016-12-31 00:00:00, the BETWEEN operator includes only rows that exactly match 2016-12-31 00:00:00 and will not include rows with other values on December 31 like 2016-12-31 09:00:00 and 2016-12-31 10:00:00.
Our intention is to retrieve all orders including the ones in December 31, 2016, but the BETWEEN operator returns the order up the the start of December 31, 2016.
To include all orders during December 31, 2016, you should use the comparison operator >= and < and shift the date to January 01, 2017.
SELECT
order_id,
customer_id,
status,
order_date
FROM
orders
WHERE
order_date >= DATE '2016-12-01'
AND order_date < DATE '2017-01-01'
ORDER BY
order_date;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To make it more clear, we’ll take an example using the between with dates that include time components.
CREATE TABLE logs (
id NUMBER GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
message VARCHAR2(100) NOT NULL,
created_at DATE NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO logs(message, created_at) VALUES ('System Started', TO_DATE('2024-01-01 08:00:00', 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS'));
INSERT INTO logs(message, created_at) VALUES ('User Login', TO_DATE('2024-01-15 14:30:00', 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS'));
INSERT INTO logs(message, created_at) VALUES ('System Shutdown', TO_DATE('2024-01-31 22:00:00', 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS'));
INSERT INTO logs(message, created_at) VALUES ('Maintenance', TO_DATE('2024-02-01 09:00:00', 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS'));Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Note that you can execute these queries in Oracle client tool such as SQL Developer. It’ll create a logs table and insert three rows into it. For now, you don’t need to understand these queries. And you’ll learn about them in the upcoming tutorials.
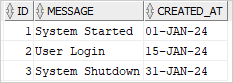
The following query uses the BETWEEN operator to get the logs between 2024-01-01 and 2024-01-31:
SELECT
*
FROM
logs
WHERE
created_at BETWEEN DATE '2024-01-01' AND DATE '2024-01-31';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)It returns only two rows:
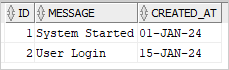
It does not return the System Shutdown on 2024-01-31 22:00:00. To fix this, you can use the >= and < operator:
SELECT
*
FROM
logs
WHERE
created_at >= DATE '2024-01-01'
AND created_at < DATE '2024-02-01';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
Summary #
- Use the Oracle
BETWEENoperator to select rows that are in a specific range. - Use the
NOToperator to negate the result of theBETWEENoperator. - Avoid using the
BETWEENoperator with date values.