Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Oracle Data Pump Export utility to unload data (and metadata) from the Oracle database.
Introduction to Oracle Data Pump Export tool
Oracle Data Pump Export is a built-in utility program for unloading data and metadata into a set of dump files. The dump file set then can be imported by the Data Pump Import utility on the same or another Oracle Database system.
The dump file set contains table data, database object metadata, and control information that are written in an Oracle-proprietary, binary format.
The Data Pump Export works on the server only, therefore, it typically deals with directory object that maps to physical directories on the database server. The Export Data Pump tool does not write to the local file system on your client computer.
Notice that Oracle introduced the Data Pump Export utility starting in Oracle 10g. The Data pump Export is a replacement for the old Export utility.
According to Oracle, the new Data Pump Export can be up to 40 times faster. Here are some notable features of the Oracle Data Pump Export tool:
- Compression of output files
- Encryption
- Export via network link
- Parallelism
- Using a subquery to export partial data.
- Renaming tables/schemas/tablespaces
Calling Data Pump Export program
You invoke the Data Pump Export program using the expdp command. The behaviors of the program are determined by the parameters specified either on the command line or in a parameter file.
expdpCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Oracle Data Pump Export example
First, create a new directory object ot_external that maps to the c:\export folder:
CREATE DIRECTORY ot_external AS 'C:\export';
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, create a parameter file named customer.par with the following contents and place the file in the C:\export directory:
userid=ot@pdborcl/Abcd1234 directory=ot_external dumpfile=customer_exp%U.dmp logfile=customer_exp.log filesize=50K tables=customers
In this parameter file:
- The first line specifies the user and password (
userid) for connecting to the Oracle database. - The second line indicates the directory object which maps to the output directory that stores the dump file set.
- The dump files will have names
customer_exp1.dmp,customer_exp2.dmp, … The sequence number is generated based on the%Uwildcard. - The log file will be
customer_exp.log. - Each dump file will have a maximum size of 40KB, just for demonstration purposes. If a dump file has a size exceeding 40K, the Data Pump Export tool will create the next dump file. The valid range of the dump files is from 40K to 16TB.
- The Data Pump Export will export only the
customerstable specified by the last line in the parameter filetables=customers.
Third, invoke the Data Pump Export program to export the customers table to the dump files:
expdp parfile=customer.par
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the dump file set:
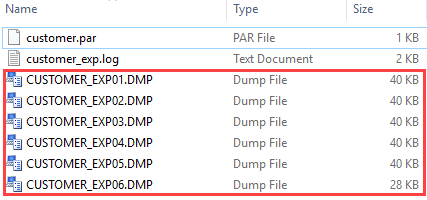
Now, it is your turn to export all objects in the OT schema to the dump files by creating a new parameter file with the following contents:
userid=ot@pdborcl/Abcd1234 directory=ot_external dumpfile=ot_exp%U.dmp logfile=ot_exp.log filesize=50K schemas=ot
Run this command:
expdp parfile=ot.parCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this tutorial, you’ve learned how to use the Oracle Data Pump Export utility program to unload data and metadata from the Oracle database.