Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the Oracle CREATE PROFILE statement to create a profile for users.
Introduction to Oracle CREATE PROFILE statement #
A user profile is a set of limits on the database resources and the user password. Once you assign a profile to a user, then that user cannot exceed the database resource and password limits.
The CREATE PROFILE statement allows you to create a new user profile. The following illustrates the basic syntax of the CREATE PROFILE statement:
CREATE PROFILE profile_name
LIMIT { resource_parameters | password_parameters};Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax:
- First, specify the name of the profile that you want to create.
- Second, specify the
LIMITon either database resources or password.
resource_parameters #
You use the following clauses to set the limit for resource parameters:
SESSIONS_PER_USER– specify the number of concurrent sessions that a user can have when connecting to the Oracle database.CPU_PER_SESSION– specify the CPU time limit for a user session, represented in hundredth of seconds.CPU_PER_CALL– specify the CPU time limit for a call such as a parse, execute, or fetch, expressed in hundredths of seconds.CONNECT_TIME– specify the total elapsed time limit for a user session, expressed in minutes.IDLE_TIME– specify the number of minutes allowed for periods of continuous inactive time during a user session. Note that the long-running queries and other operations will not be subject to this limit.LOGICAL_READS_PER_SESSION– specify the allowed number of data blocks read in a user session, including blocks read from both memory and disk.LOGICAL_READS_PER_CALL– specify the allowed number of data blocks read for a call to process a SQL statement.PRIVATE_SGA– specify the amount of private memory space that a session can allocate in the shared pool of the system’s global area (SGA).COMPOSITE_LIMIT– specify the total resource cost for a session, expressed in service units. The total service units are calculated as a weighted sum ofCPU_PER_SESSION,CONNECT_TIME,LOGICAL_READS_PER_SESSION, andPRIVATE_SGA.
password_parameters #
You use the following clauses to set the limits for password parameters:
FAILED_LOGIN_ATTEMPTS– Specify the number of consecutive failed login attempts before the user is locked. The default is 10 times.PASSWORD_LIFE_TIME– specify the number of days that a user can use the same password for authentication. The default value is 180 days.PASSWORD_REUSE_TIME– specify the number of days before a user can reuse a password.PASSWORD_REUSE_MAX– specify the number of password changes required before the current password can be reused. Note that you must set values for bothPASSWORD_REUSE_TIMEandPASSWORD_REUSE_MAXparameters make these parameters take effect.PASSWORD_LOCK_TIME– specify the number of days that Oracle will lock an account after a specified number of consecutive failed logins. The default is 1 day if you omit this clause.PASSWORD_GRACE_TIME– specify the number of days after the grace period starts during which a warning is issued and login is allowed. The default is 7 days when you omit this clause.
Note that to create a new profile, your user needs to have the CREATE PROFILE system privilege.
Oracle CREATE PROFILE examples #
To find the current profile of a user, you query it from the dba_users view as shown in the following statement:
SELECT
username,
profile
FROM
dba_users
WHERE
username = 'OT';
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
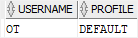
So the user OT has the DEFAULT profile.
When you create a user without explicitly specifying a profile, Oracle will assign the DEFAULT profile to the user.
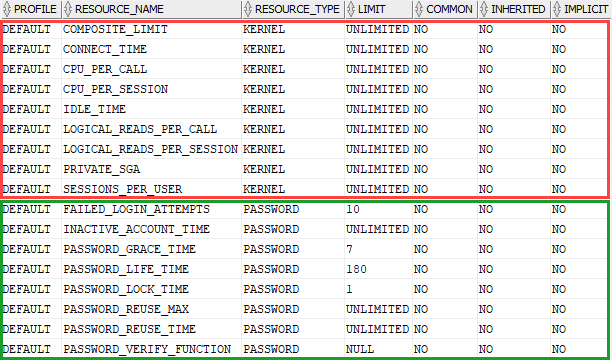
To find the parameters of DEFAULT profile, you query the dba_profiles as shown in the following query:
SELECT
*
FROM
dba_profiles
WHERE
PROFILE = 'DEFAULT'
ORDER BY
resource_type,
resource_name;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
1) Using Oracle CREATE PROFILE to set the resource limit example #
First, create a profile called CRM_USERS that set the resource limits:
CREATE PROFILE CRM_USERS LIMIT
SESSIONS_PER_USER UNLIMITED
CPU_PER_SESSION UNLIMITED
CPU_PER_CALL 3000
CONNECT_TIME 15;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, create a user called CRM:
CREATE USER crm IDENTIFIED BY abcd1234
PROFILE crm_users;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Third, verify the profile of the CRM user:
SELECT
username,
profile
FROM
dba_users
WHERE
username = 'CRM';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)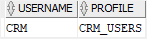
The user CRM is subject to the following limits: the CRM user can have any number of concurrent sessions (SESSIONS_PER_USER). In each session, it can consume any amount of CPU time (CPU_PER_SESSION). In addition, the CRM user cannot consume more than 30 seconds of CPU time in a single call. (CPU_PER_CALL) and each session cannot last for more than 15 minutes.
2) Using Oracle CREATE PROFILE to set the password limit example #
First, create a new profile called erp_users with password limits:
CREATE PROFILE erp_users LIMIT
FAILED_LOGIN_ATTEMPTS 5
PASSWORD_LIFE_TIME 90;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Then, create a user named sap and set its profile to erp_users:
CREATE USER sap IDENTIFIED BY abcd1234
PROFILE erp_users;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The sap user is subject to the following password limits:
- The number of consecutive failed login attempts (
FAILED_LOGIN_ATTEMPTS) is 5 before the account is locked. - The number of days to change the password is 90 days.
In this tutorial, you’ve learned how to use Oracle CREATE PROFILE to set resource and password limits to users.